On February 21, 2025, Professor Chen Minglong and his team from the First Affiliated Hospital with Nanjing Medical Universitypublished a groundbreaking research paper titled “Telemedicine-Based Integrated Management of Atrial Fibrillation in Village Clinics: ACluster Randomized Trial” in Nature Medicine, a top-tier international medical journal. In this study, Professor Chen’s team innovatively developed a telemedicine-based, village doctor-led integrated management model for atrial fibrillation (AF) and validated its effectiveness through a standardized cluster randomized controlled trial (the MIRACLE-AF study). This model holds great potentialfor providing solutionsto chronic disease management in rural or medically underserved areas worldwide.

Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a common arrhythmia closely associated with an increased risk of stroke and mortality. In China, approximately 1.6% of adults (about 18 million people) are affected by AF. Professor Chen’s team conducted a survey on AF prevalence in rural China, which revealed that the rate among elderly individuals aged 65 and above in rural areas is as high as 4.3%. However, the compliance rate for comprehensive AF management among the elderly in these regions is a mere 1.7%. Given that rural healthcare in China heavily relies on village doctors, whose capabilityfor chronic disease management is limited, providing optimized AF management remains a major challenge.
To address this issue, Professor Chen’s team developed an innovative management model that leverages a telemedicine platform, supported by AF specialists and led by village doctors, with the goal ofimproving the compliance of rural elderly patients with comprehensive AF management.
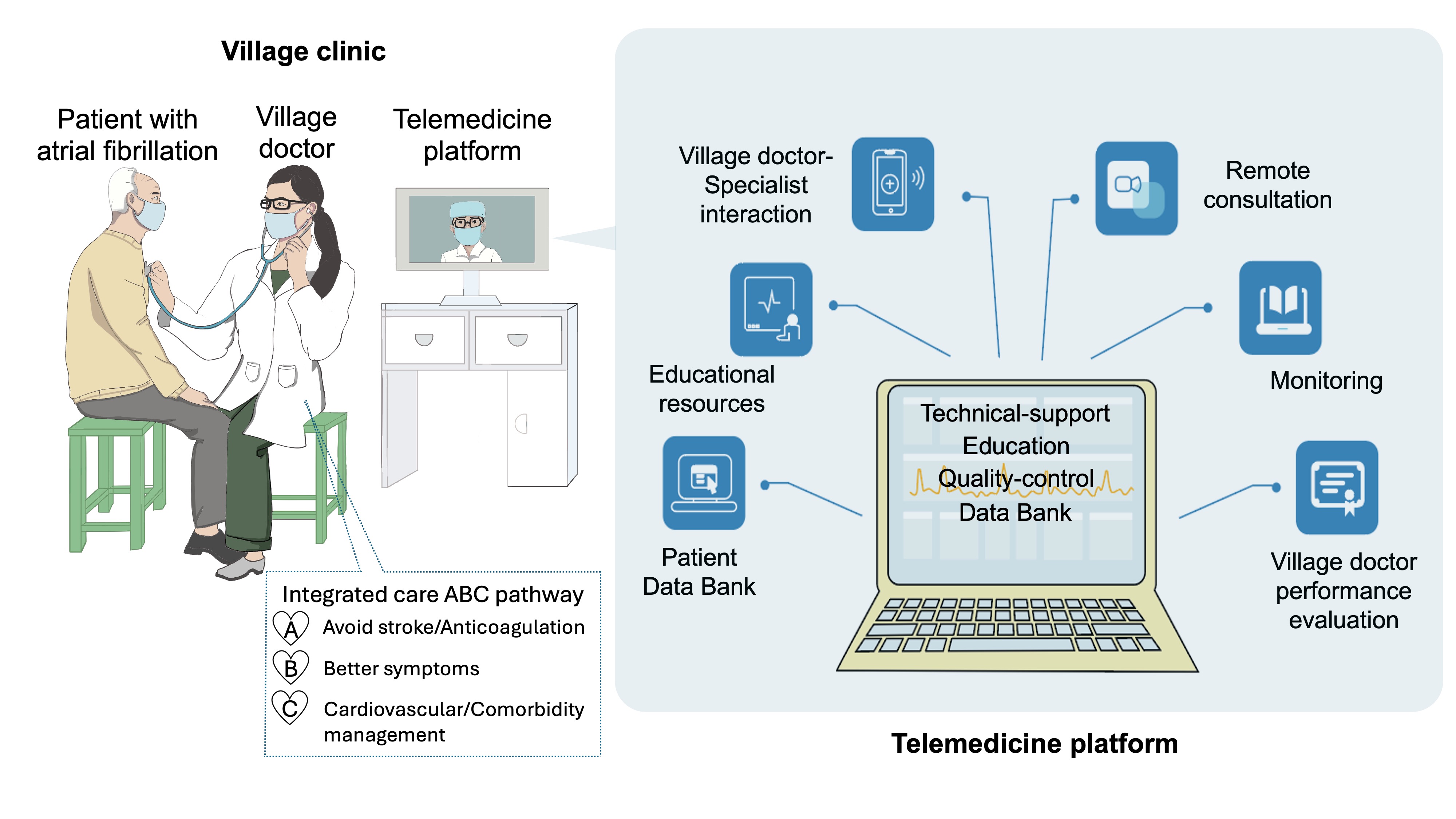
This study was a prospective, cluster-randomized clinical trial involving 30 village clinics in Jiangdu District, Yangzhou City, Jiangsu Province, and 1,039 AF patients aged 65 and above. The 36-month follow-up results demonstrated that the new management model reduced the incidence of major cardiovascular and cerebrovascular endpoint events by 36% and the risk of cardiovascular death by 50%, compared to the usual care model.
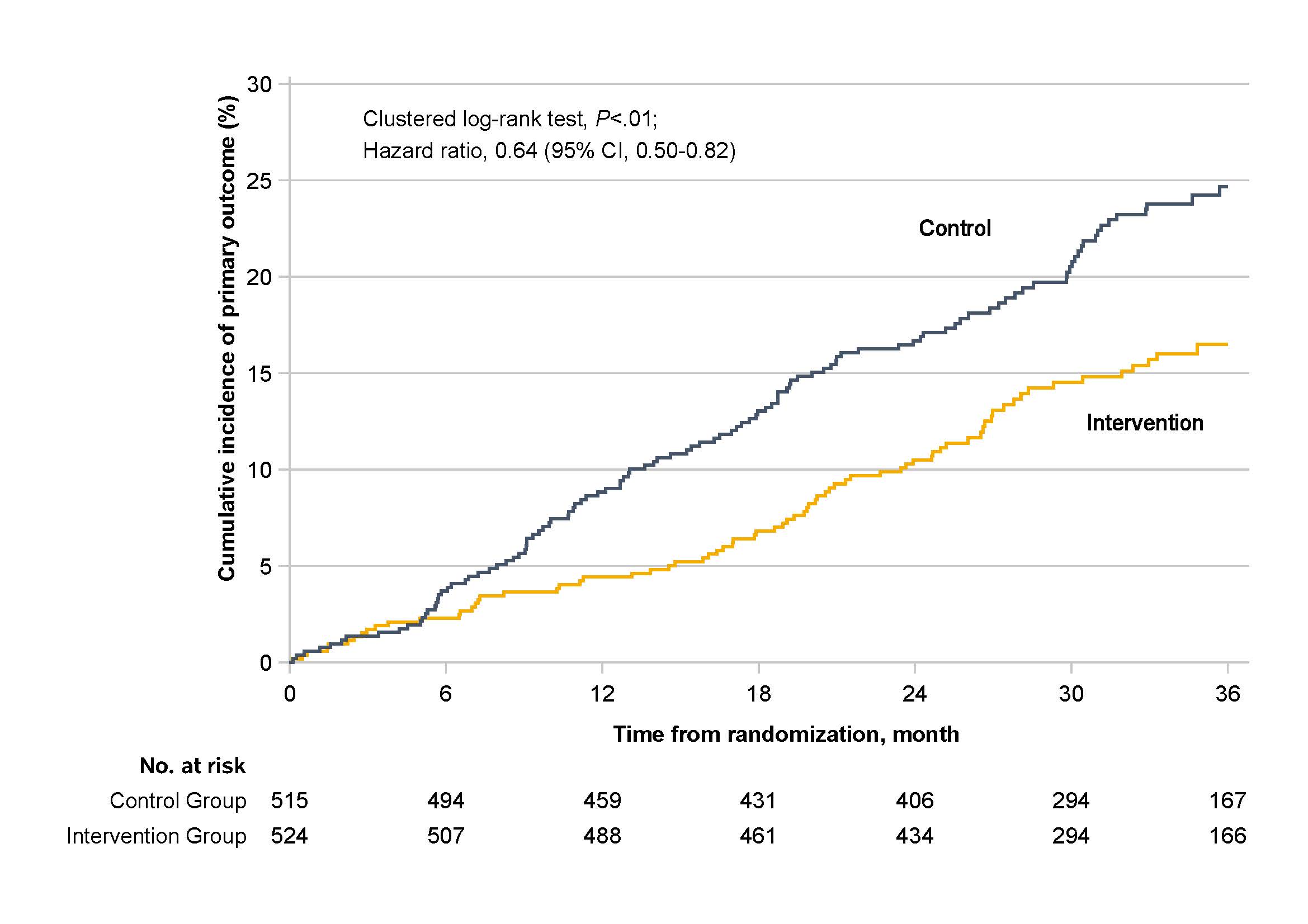
The MIRACLE-AF study is a pioneering effort that establishes a new model for integrated chronic disease management through telemedicine.This approach delivers high-quality medical resources to underserved areas, directly improving healthcare services and health outcomes for vulnerable populations, with the potential for broad application.

Professor ChenMinglong and Professor LiMingfang from the Department of Cardiology at the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, along with Gregory Y. H. Lip, Professorat the University of Liverpool, UK, are the co-corresponding authors of the paper. The co-first authors are ChuMing and ZhangShimeng from the Department of Cardiology at the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, andGong Jinlong from the Department of Cardiology at Jiangdu People’s Hospital,affiliated with Yangzhou University. This study received strong support from Professor Chen’s team, the Jiangdu Commission of Health, Jiangdu People’s Hospital, the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Taizhou People’s Hospital (affiliated with Nanjing Medical University), and Professor PengZhihang’s team from the Department of Biostatistics at the School of Public Health, Nanjing Medical University.
For the full article, please click here: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-025-03511-2
(Drafted by Prof. LiMingfang; Reviewed by Prof. ChenMinglong; Translation revised by Zhang Bei)



