A research team led by Professor Li Xinli and Zhang Haifeng from the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University/Jiangsu Province Hospital has recently published a groundbreaking paper titled “QUEST: Qiliqiangxin in Heart Failure: Assessment of Reduction in Mortality”in the esteemed journal Nature Medicine. This study is the first to demonstrate the clinical efficacy and safety of the traditional Chinese medicine Qiliqiangxin Capsule (QLQX) for patients with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction (HFrEF) using an internationally recognized clinical trial design.The findings provide new intervention strategies and highlight the value of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) in heart failure treatment. This publication marks a significant recognition of TCM within the global medical community.

Heart failure (HF) is a severe cardiovascular condition associated with high morbidity and mortality. While existing treatments can improve patient outcomes, significant residual risks persist. QLQX are an original TCM formulation based on Luobin theory and have been approved by the NMPA for the treatment of chronic heart failure in China since 2004. Supported by a National Key R&D Project, the QUEST study has further validated QLQX’s clinical efficacy in HFrEF patients using modern evidence-based medical methods.
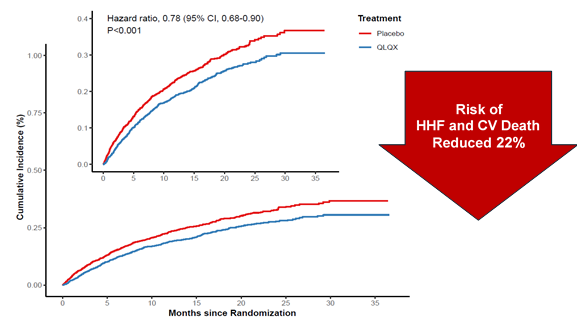
The QUEST study is a large-scale, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trial conducted across 133 clinical centers in Chinese mainland and Hong Kong SAR, China, involoving 3,110 HFrEF patients. The results revealed that adding Qiliqiangxin capsules to standard treatment significantly reduced the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (a composite endpoint of cardiovascular death and heart failure rehospitalization) by 22%, decreased heart failure hospitalization rate by 24%, and lowered the risk of cardiovascular death by 17%. These results highlight the clinical efficacy of QLQX. Additionally, the capsules did not significantly increase adverse events compared to the placebo group, confirming their safety and tolerability.
At the European Society of Cardiology (ESC 2023) conference held in Amsterdam, Netherlands, last August, Professor Li Xinli presented the significant findings of the QUEST study during the HOT LINE heart failure session. Systemic mechanistic studies have suggested that QLQX may exert their effects by modulating the PPARγ/PGC-1α signaling pathway. The success of the QUEST study has since attracted widespread attention and discussion within the international medical community, offering new insights into integrating traditional Chinese and modern medicine in heart failure treatment.
The QUEST study represents a milestone in the use of TCM for heart failure. It not only validates the clinical value of QLQX but also paves the way for the internationalization and standardization of TCM. The successful publication of these findings signifies a significant global recognition of TCM and lays a crucial foundation for the future integration of traditional and modern medicine in treating cardiovascular diseases. We look forward to more innovative TCM achievements like Qiliqiangxin capsules that can bring hope to patients worldwide and contribute to the global health and well-being.
Prof. Li Xinli (李新立) and Prof. Zhang Haifeng (张海锋) from the Department of Cardiology are the co-corresponding authors of this paper, with Postdoctoral Fellow Iokfai Cheang (郑旭辉), Associate Chief Physician Yao Wenming (姚文明), and Chief Physician Zhou Yanli (周艳丽) serving as co-first authors. This research was supported by the National Key Technologies R&D Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Collaborative Innovation Center for Cardiovascular Disease Translational Medicine, and the State Key Laboratory for Innovation and Transformation of Luobing Theory.
Full Article:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-024-03169-2
[Drafted by the First Affiliated Hospital of NMU; Reviewed by Professor Li Xinli;Translated by Dr. Iokfai Cheang]



